Introduction: What is gynecomastia and why does it matter?
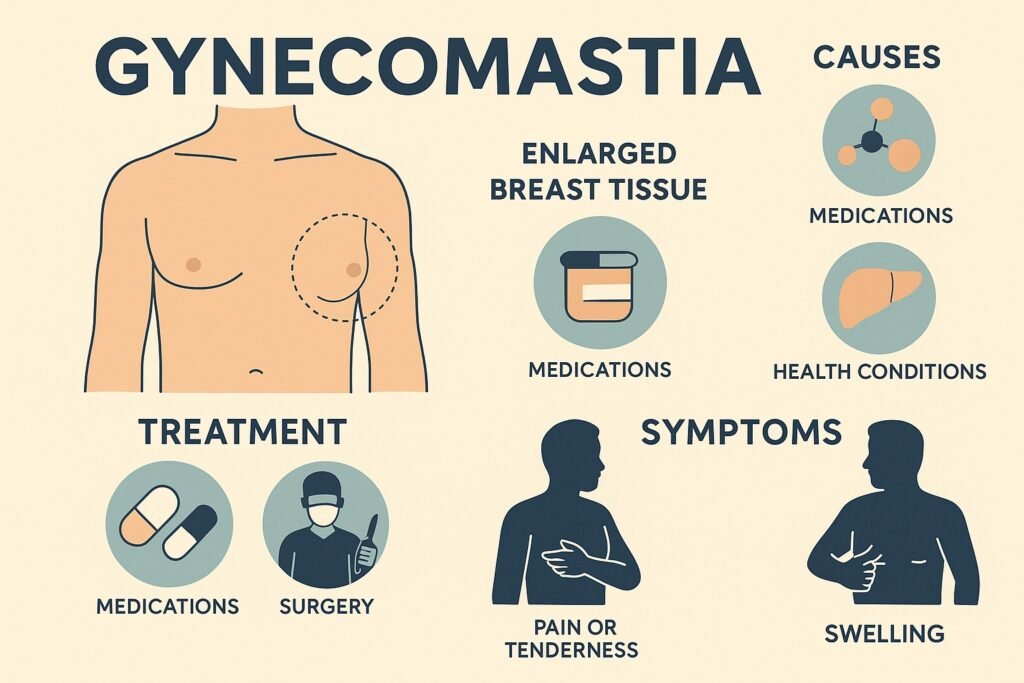
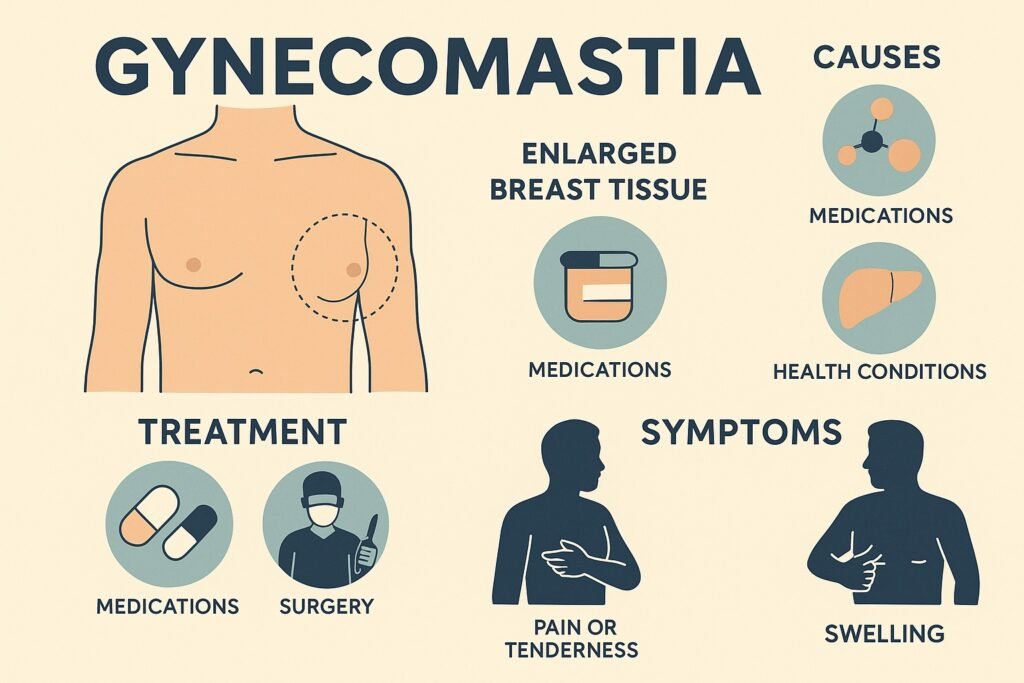
Gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of male breast tissue. Though it may seem like a minor issue, it can affect physical comfort, posture, and self-confidence. While not life-threatening, gynecomastia often leads men to avoid certain clothes or social situations. In many cases, the condition is reversible through surgery or medication. As awareness grows, more patients are seeking solutions and education is a key part of that journey.
1. Understanding the root causes
Gynecomastia happens when there’s a hormonal imbalance between estrogen and testosterone. This imbalance can stem from multiple sources:
- Puberty: Hormonal shifts during adolescence may trigger temporary breast tissue growth.
- Aging: Older men may naturally experience decreased testosterone.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like anti-androgens, antidepressants, or anabolic steroids, can cause gynecomastia.
- Health conditions: Liver disease, kidney failure, or thyroid disorders may also play a role.
Before: Many believed gynecomastia was purely due to fat.
After: We now know it’s often a hormonal issue and not necessarily linked to weight.
2. Is it gynecomastia or pseudogynecomastia?
Not all chest fullness in men is true gynecomastia. Some patients may have pseudogynecomastia, where fat—not glandular tissue—is the primary cause. Here’s how they differ:
| Condition | Cause | Tissue Type | Treatment |
| Gynecomastia | Hormonal imbalance | Glandular | Surgery or meds |
| Pseudogynecomastia | Weight gain | Fat | Liposuction, diet |
Ultrasound and physical exams help doctors distinguish between the two. A proper diagnosis ensures patients get the right treatment and avoid unnecessary procedures.
3. Treatment options: from medication to surgery
Medications
In early stages, hormone-modulating drugs like tamoxifen may help reduce tissue growth. However, results are often modest and best suited for recent-onset cases.
Liposuction
Ideal for pseudogynecomastia, liposuction removes fatty tissue with minimal scarring. Recovery is relatively quick, often within 1–2 weeks.
Glandular excision
For true gynecomastia, surgery to remove the breast gland delivers long-term results. This procedure may include:
- A small incision around the areola
- Use of ultrasonic or tumescent-assisted liposuction
- Outpatient operation under local or general anesthesia
Before: Surgery was seen as extreme. After: It’s now a common, low-risk procedure with high satisfaction rates.
4. Post-op care and recovery expectations
After gynecomastia surgery, patients typically follow a structured aftercare plan:
- Wear a compression garment for 2–4 weeks to reduce swelling
- Avoid heavy lifting or upper body workouts for 3–4 weeks
- Apply scar-reducing cream as recommended
- Follow up with ultrasound or manual exams
Most patients return to desk jobs in a few days and resume full activity in about a month. Education plays a big role here—knowing what to expect helps reduce anxiety and avoid complications.
5. Psychological impact and confidence rebuilding
Beyond physical benefits, gynecomastia surgery has a deep emotional impact. Patients often report:
- Improved posture and body language
- Less anxiety in social situations
- A renewed interest in fitness or fashion
In fact, the success of treatment is often measured not just by appearance, but by how patients feel afterward.
Before: Many suffered in silence, unaware of treatment options. After: Now, patients speak openly and confidently after surgery.
Conclusion: Education leads to better outcomes
Gynecomastia (“여유증”) is common, treatable, and no longer taboo. Whether you’re dealing with glandular growth or fat buildup, identifying the cause is step one. With the right education, patients can choose treatments that match their needs, follow proper recovery, and rebuild both their bodies and confidence. In 2025, the future of gynecomastia care is bright, and it begins with informed decisions.